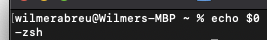
first see what bash you are using
echo $0for mac osx big sur its
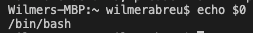
when using vscode on that same mac
https://flaviocopes.com/shell-environment-variables/

running “ls” in /etc dir you get this
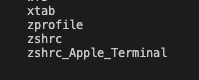
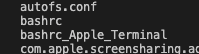
depending on what shell you use, you want to set up your env vars in those files
when search “zsh is better than bash or newer” I get this
zsh: For the most part bash and zsh are almost identical which is a relief. … The commands you learned for bash will also work in zsh although they may function differently on output. Zsh seems to be much more customizable than bash
so because of that lets use zsh
sudo suput in password
touch /etc/werm && chmod a+x /etc/werminsert this code into /etc/werm. It allows for you to set a dir that gets combed and if there are any files in there with .sh ext get executed.
for i in /etc/werm.d/*.sh ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null 2>&1
fi
fi
donecreate a folder and file
mkdir /etc/werm.d && touch /etc/werm.d/werm.path.shinsert this into werm.path.sh
personal=/Users/wilmerabreu
export personal
scripts=/usr/local/bin/werm
export scripts
PATH=$PATH:$scripts
export PATHsave file
vim ~/.bashrctype “. /etc/werm”
vim ~/.zshrcand type in the same “./etc/werm”. Save file.
now when you open up a new bash or zsh terminal it will allow for all scripts in $scripts to be executed
werm-wnow this only works for the current user, if you create another user this will not work.